4. States of Consciousness (Ch 4)
4.1 Sleep and Dreaming
Consciousness
- A state of awareness about ourselves and our environment
- Many varieties of consciousness, both natural and induced
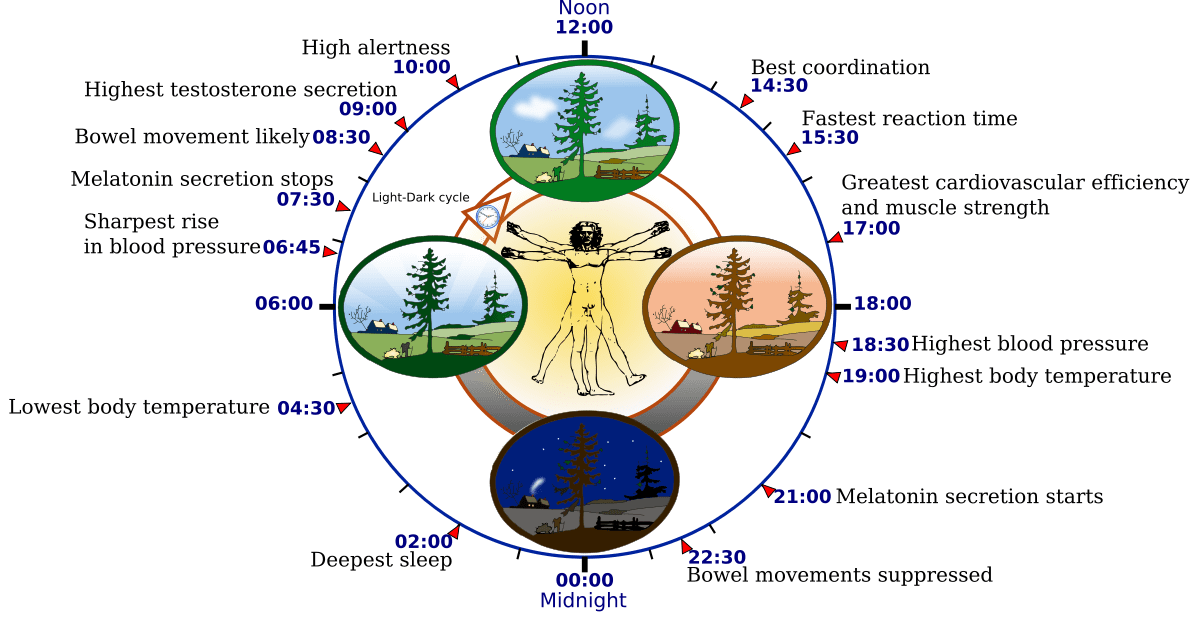
Circadian Rhythms
Body’s natural cycle of fluctuations of natural processes
- Temperature
- Hormone levels
- Level of wakefulness
About 25 hour clock when under “Free Running” conditions
Biological rhythms of sleep as measured by EEG
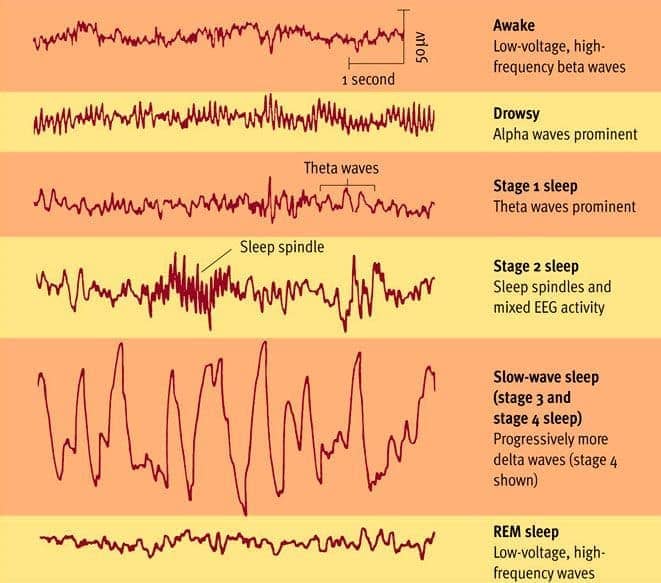
Five stages of sleep and differing brain waves
Stage 1: Alpha waves
- hypnogogic sensations
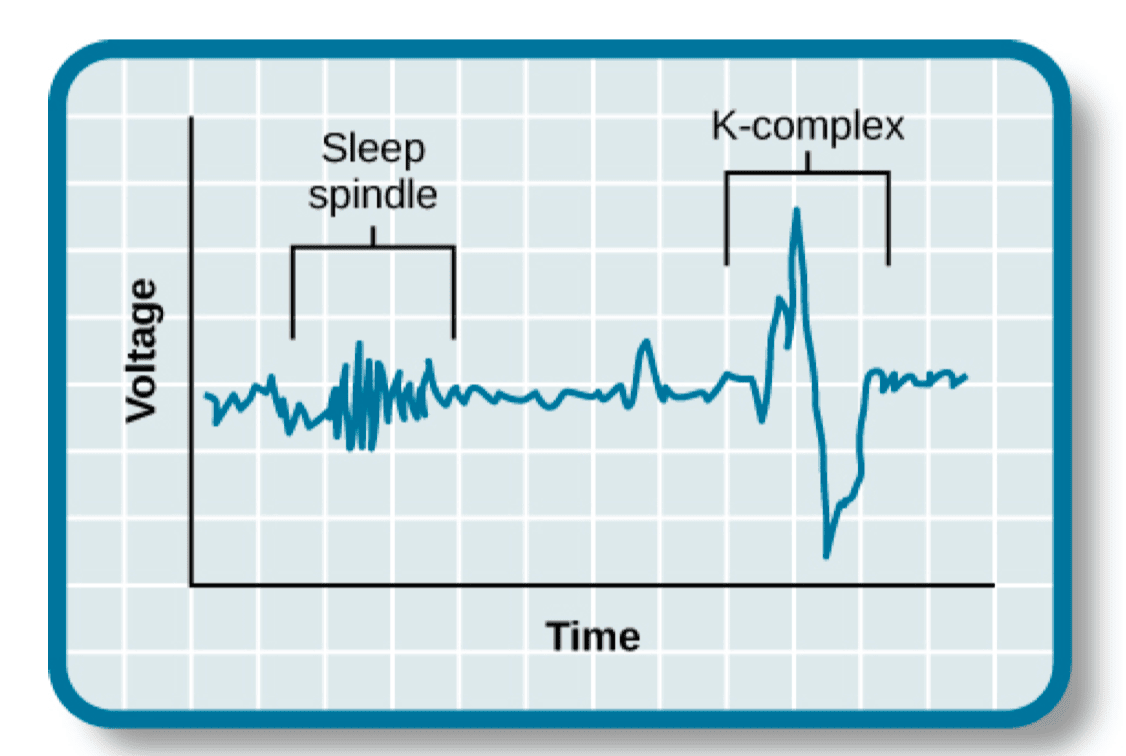
Stage 2: Theta waves
- sleep spindles
- K-complexes
Stage 3: delta waves
Stage 4: slow wave sleep
REM: paradoxical sleep
Sleep disorders
- insomnia
- hypersomnia
- narcolepsy
- sleep apnea

REM rebound
- dreams appear necessary
- If REM deprived, longer periods will occur
Theories about Dreaming
- Freud’s theory of dreams
- manifest content disguised as latent content

- Activation-synthesis theory
- Constructed story to explain images from random neural activation
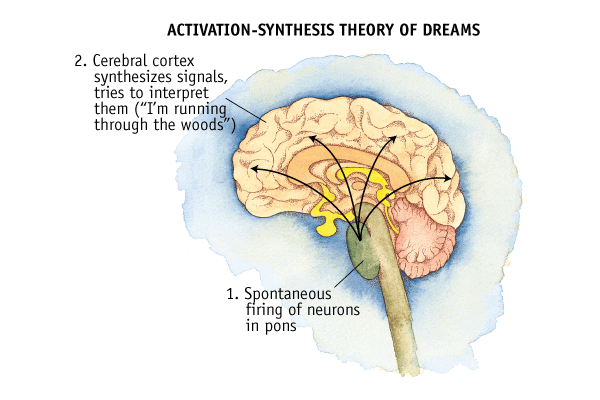
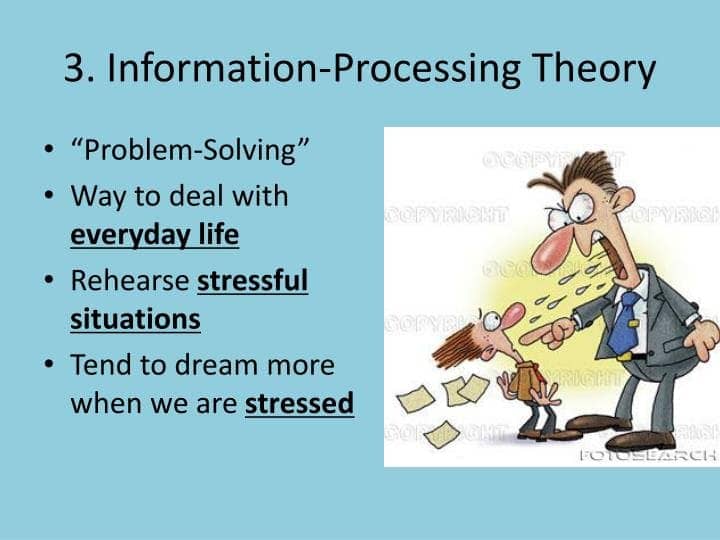
- Information-processing model
- dreams are a way to consolidate information
- Freud’s theory of dreams
4.2. Hypnosis and meditation
Hypnosis
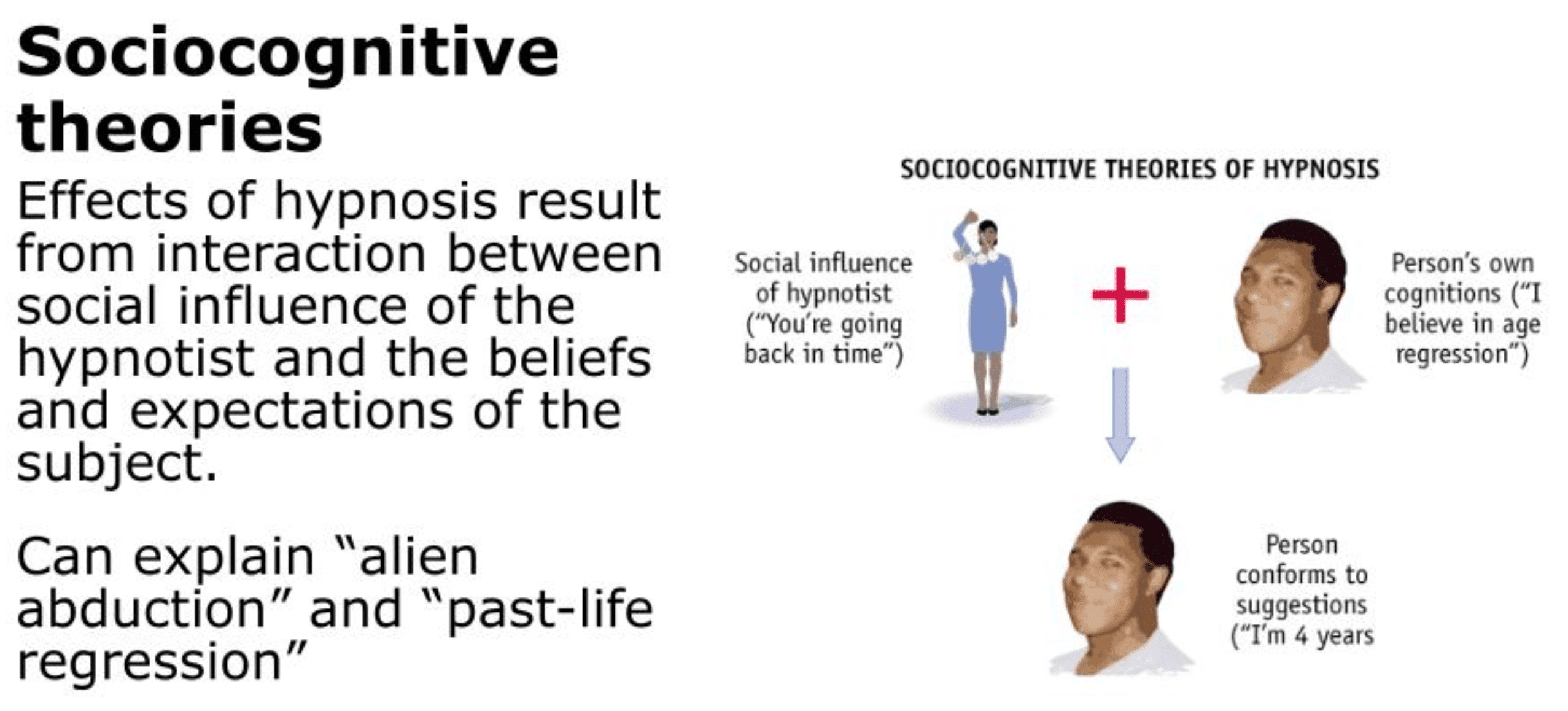
induced state of consciousness
heightened state of motivation
deep relaxation and heightened suggestibility
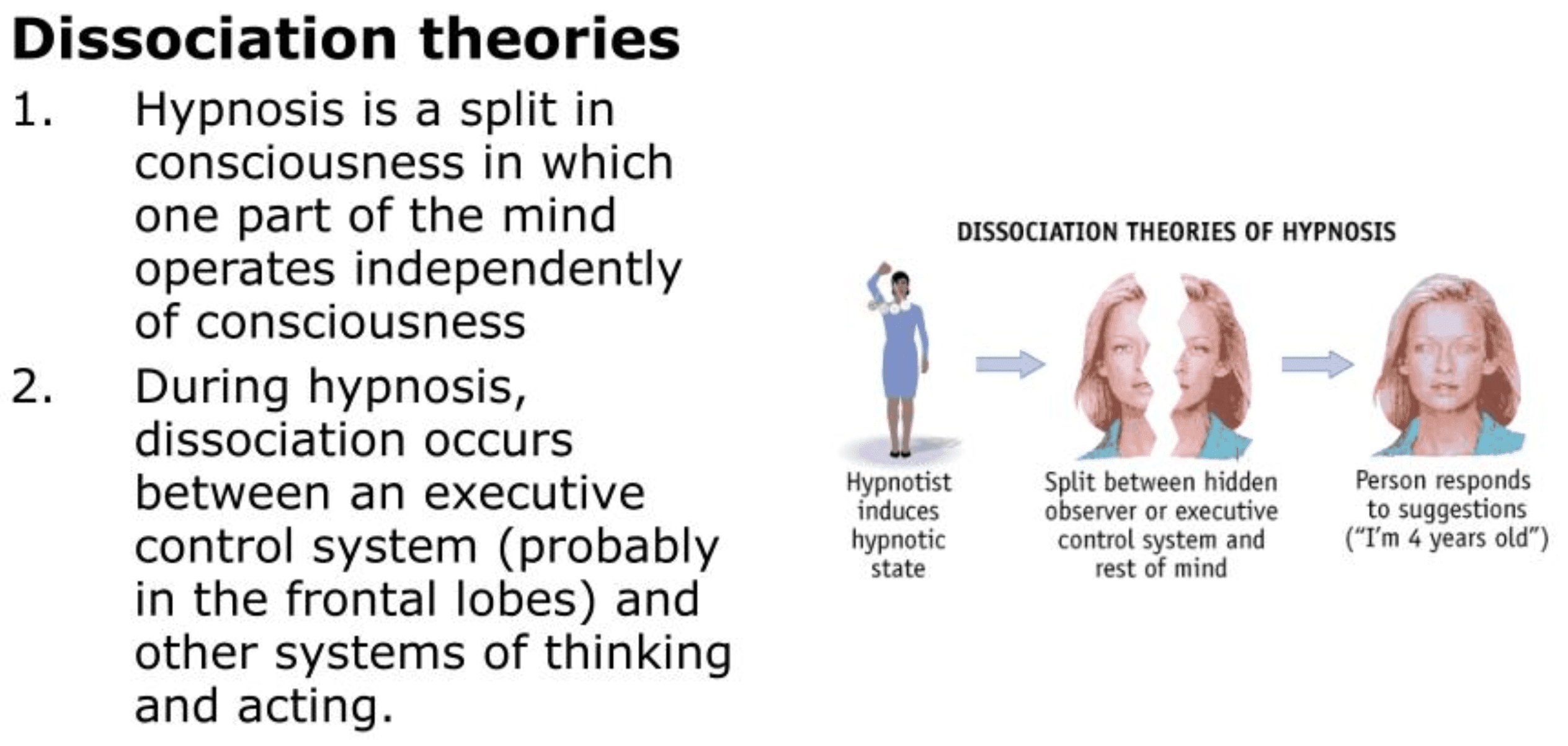
dissociation: split in consciousness
Meditation
- heightening ones' awareness
- practice of acknowledging content of the mind
- promote relaxation, energy and compassion
4.3. Psychoactive Drug Effects
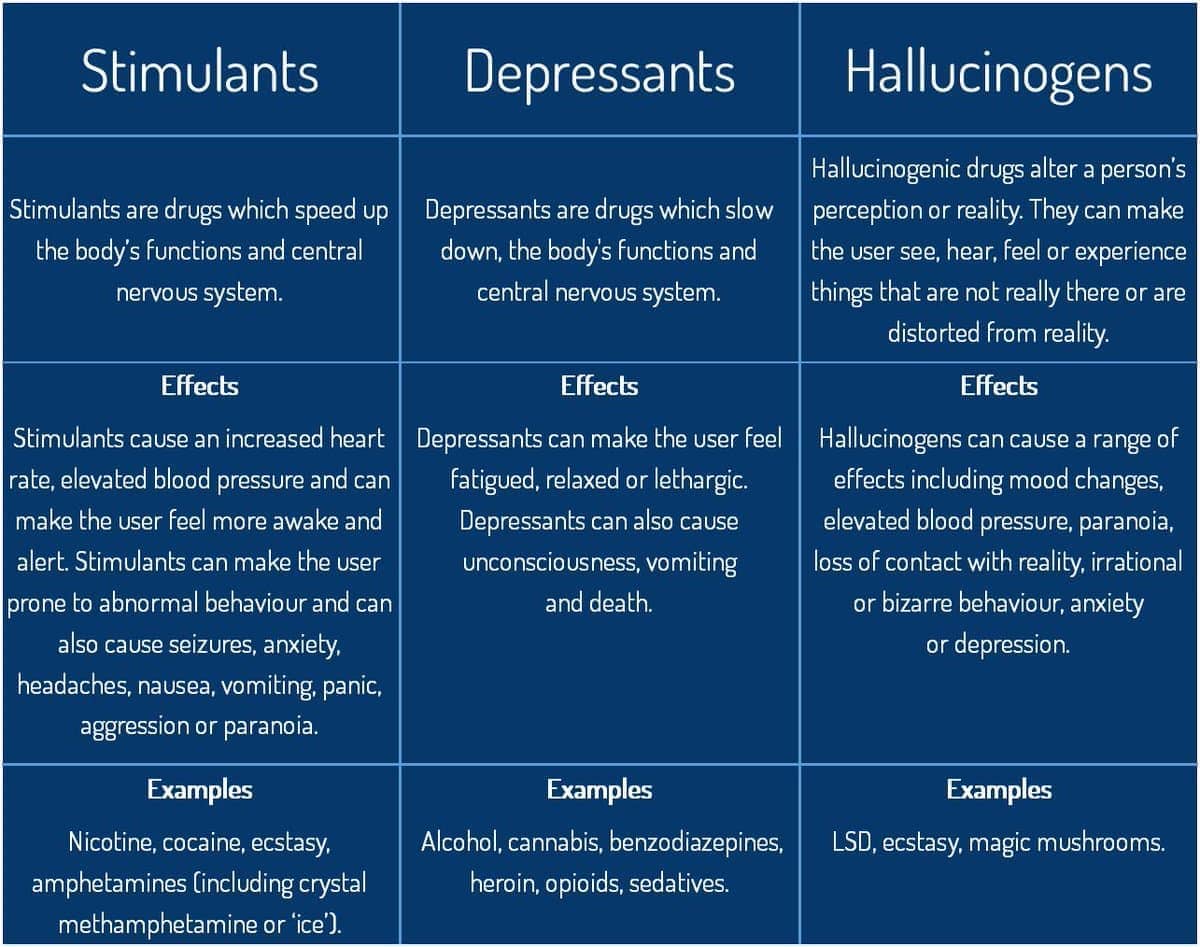
Produce a different state of consciousness by mimicking, inhibiting or stimulating activity of neurotransmitter
Depressants: alcohol, barbiturates, opiates
Stimulants: cocaine, amphetamines
Hallucinogens: LSD, mescaline, psilocybin
Quiz
- According to current psychological research, hypnosis is most useful for which of the following purposes?
- (A) Pain control
- (B) Age regression
- (C) Treatment of psychotic behavior
- (D) Treatment of a memory disorder
- (E) Treatment of a personality disorder
- Which of the following drugs is most likely to cause hyperalertness, agitation, and general euphoria?
- (A) A barbiturate
- (B) A stimulant
- (C) A hallucinogen
- (D) An antidepressant
- (E) An antipsychotic
- Brain waves during REM sleep generally appear as
- (A) alternating high- and low-amplitude waves
- (B) rapid low-amplitude waves
- (C) irregular medium-amplitude waves
- (D) slow low-amplitude waves
- (E) slow high-amplitude waves
- According to the activation-synthesis hypothesis of dreaming, dreams serve which of the following purposes?
- (A) To protect the ego from the unconscious struggles of the mind
- (B) To make sense of random neural activity during sleep
- (C) To provide unfiltered problem solving of encounters that occurred while awake
- (D) To provide a window into the unconscious, revealing true wishes and desires
- (E) To provide learning and rehearsal of material encountered while a person is awake