7. Motivation and Emotion (Ch 10)
7.1 Theories of Emotion
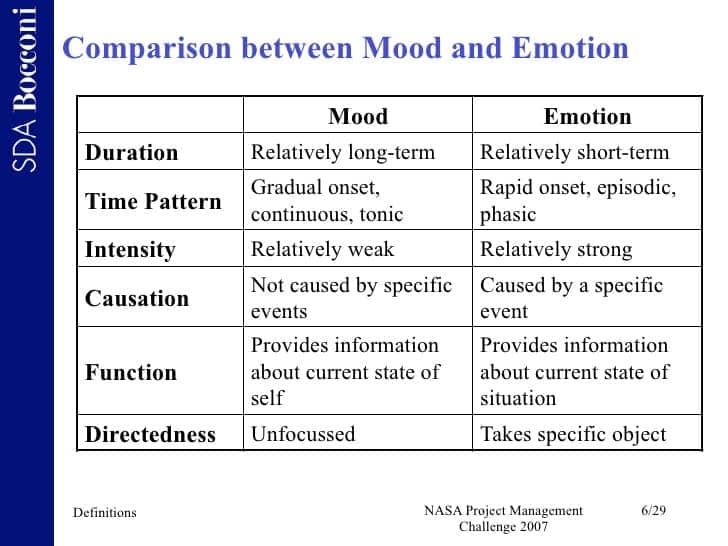
- Emotion: a psychological state involving three distinct components
- subjective experience
- physiological response
- behavioral or expressive feature
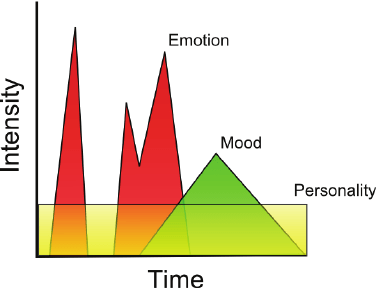
- Mood
- prolonged, less explicit, affective state
- not usually determined by a single event
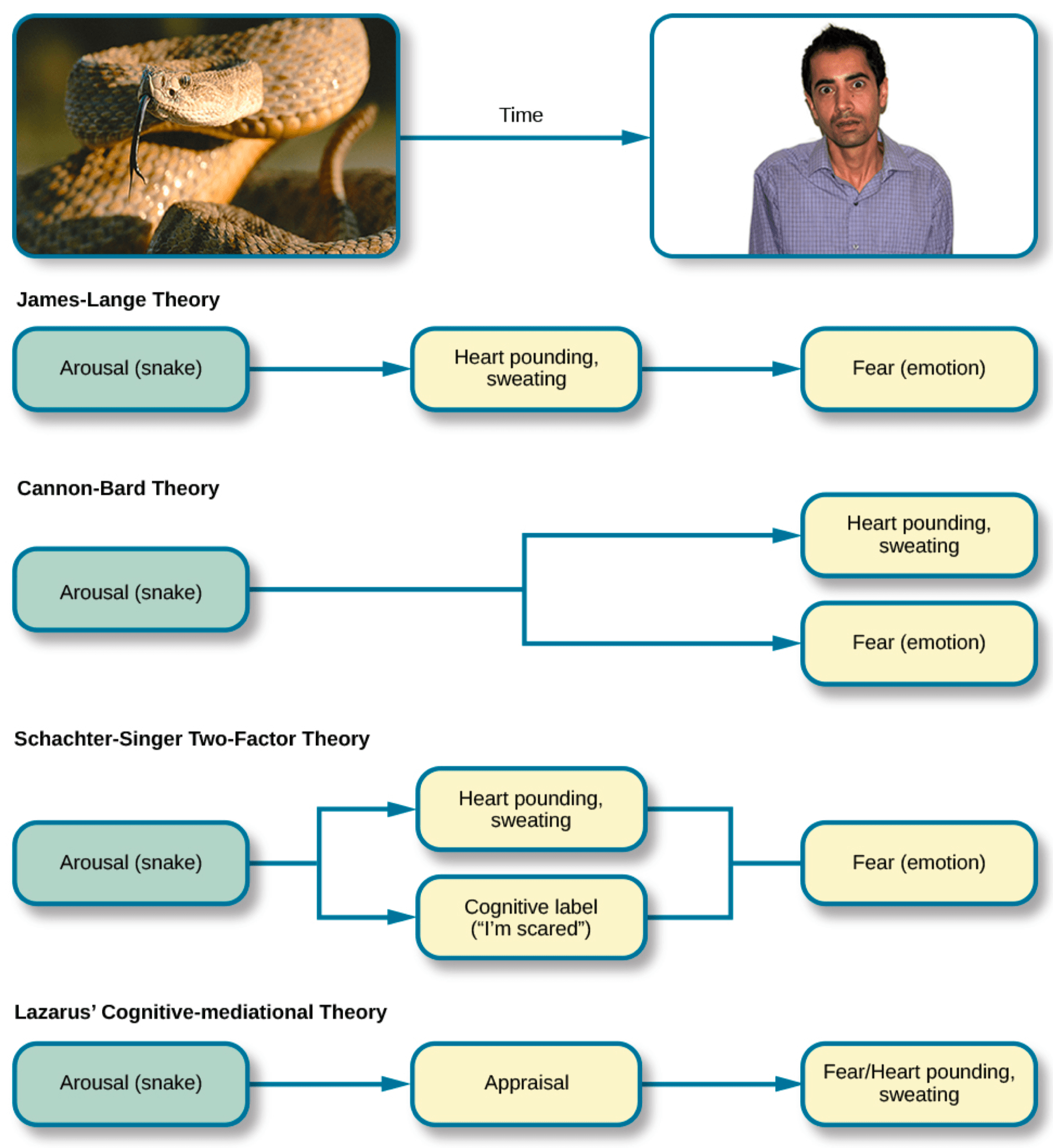
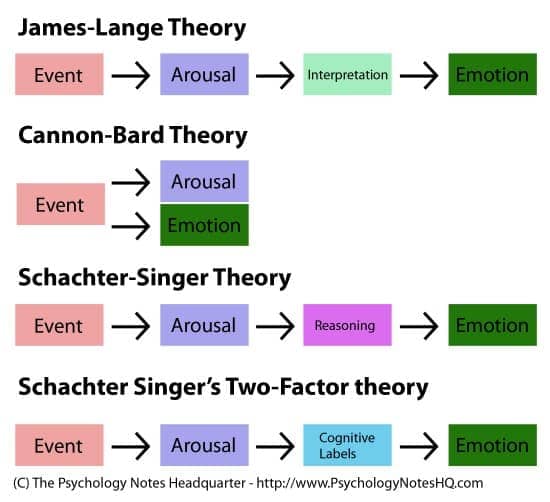
James-Lange theory
- stimulus causes arousal → emotion
- facial feedback hypothesis
Cannon- Bard theory
- relevant stimulus generate arousal
- information sent to central nervous system and cortex
- "It's a cannon"
Two-factor theory
- quality of emotional experience depends on how arousal is labeled
excitation transfer
7.2 Theories of Motivation
What drives us? What makes us behave as we do?
Motivation
- Describes the wants or needs that direct behavior towards a goal
Drive theory
- deviations from homeostasis create physiological needs to regain balance
- e.g., no food → blood sugar⬇️ → hunger
habit- likely to engage in previous behaviors that met need
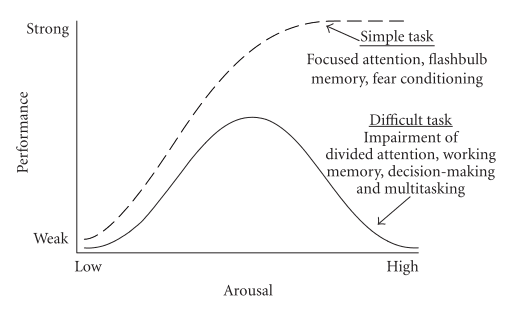
Yerkes-Dodson law
- optimal arousal levels depend on complexity and difficulty of task
- complex task→ low arousal
- simple task→ high arousal
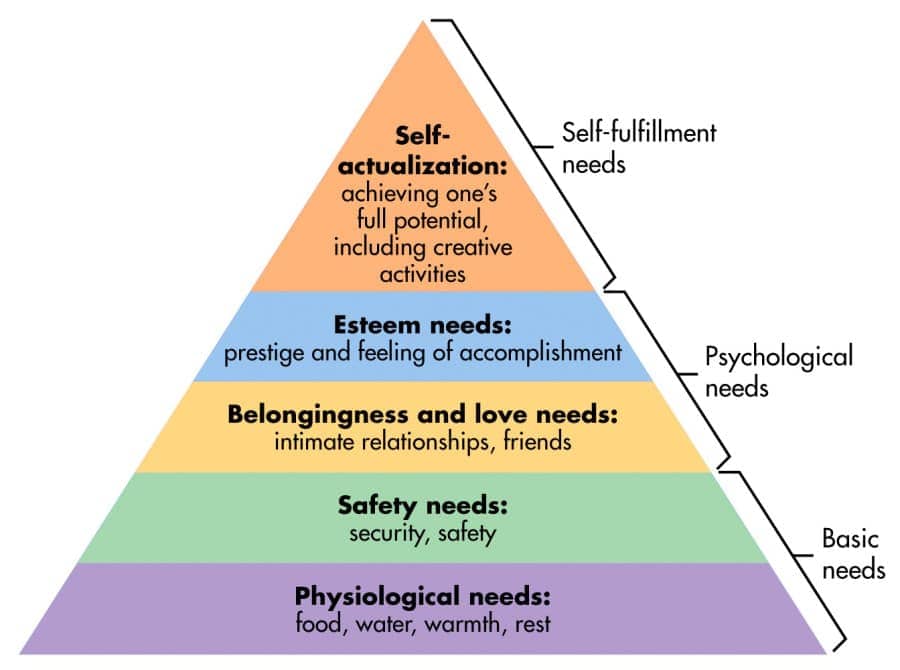
- Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
- physiological needs→ basic needs→ self-actualization
- ongoing lifelong process
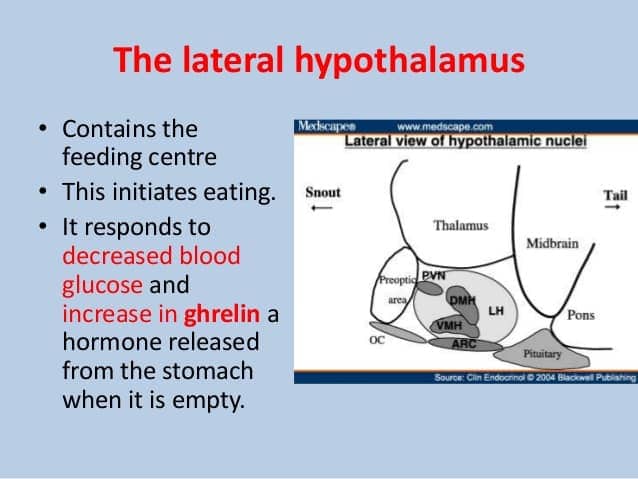
7.3 Biological Bases: Hunger, Thirst, Sex, Pain
Hunger
- biological instinct for survival
- empty stomach → hunger pains and chemicals that initiate hunger in brain
- glucose: blood sugar from food that provides energy for body
- insulin: helps reduce glucose levels thus impacting hunger
- hypothalamus
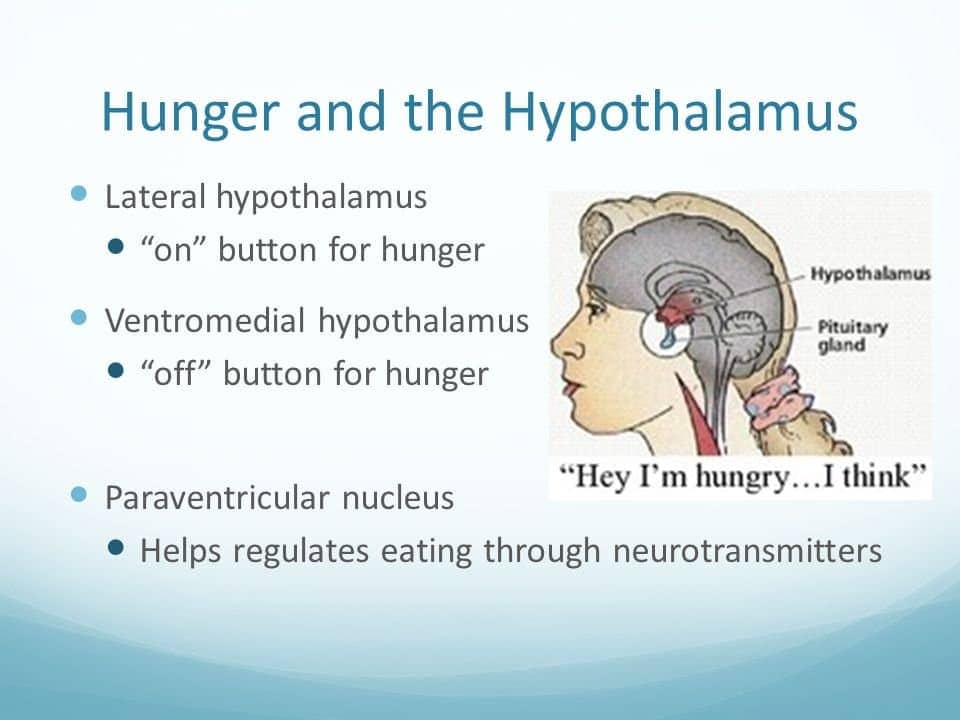
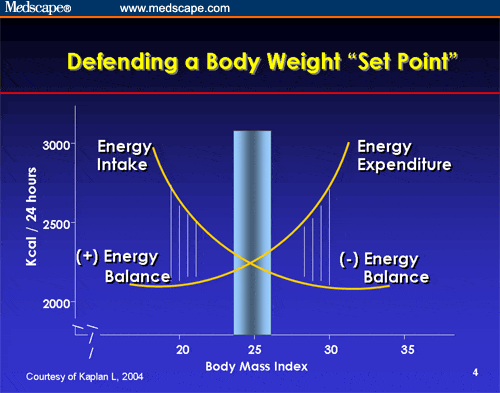
- set-point: weight your body works to maintain
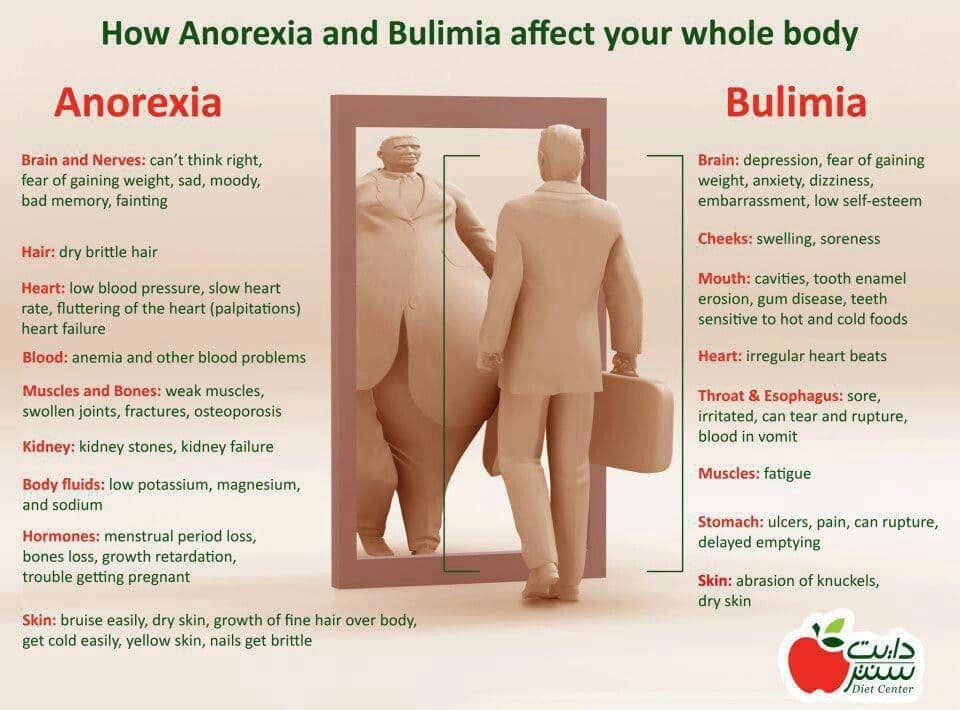
- Eating Disorders
- social and cultural pressures for ideal beauty
- anorexia, bulimia, binge eating disorder
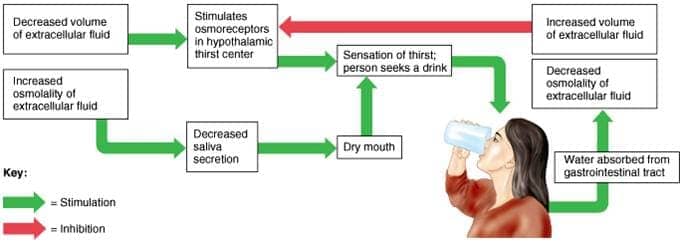
Thirst
- Produced by depletion of fluid outside and within cells
- Peripheral and central nervous system
- subfornical organ and lateral hypothalamic nucleus
- Angiotensin: produced by the kidneys
Sexual behavior
Sexual motivation from Limbic System
- amygdala
- nucleus accumbens
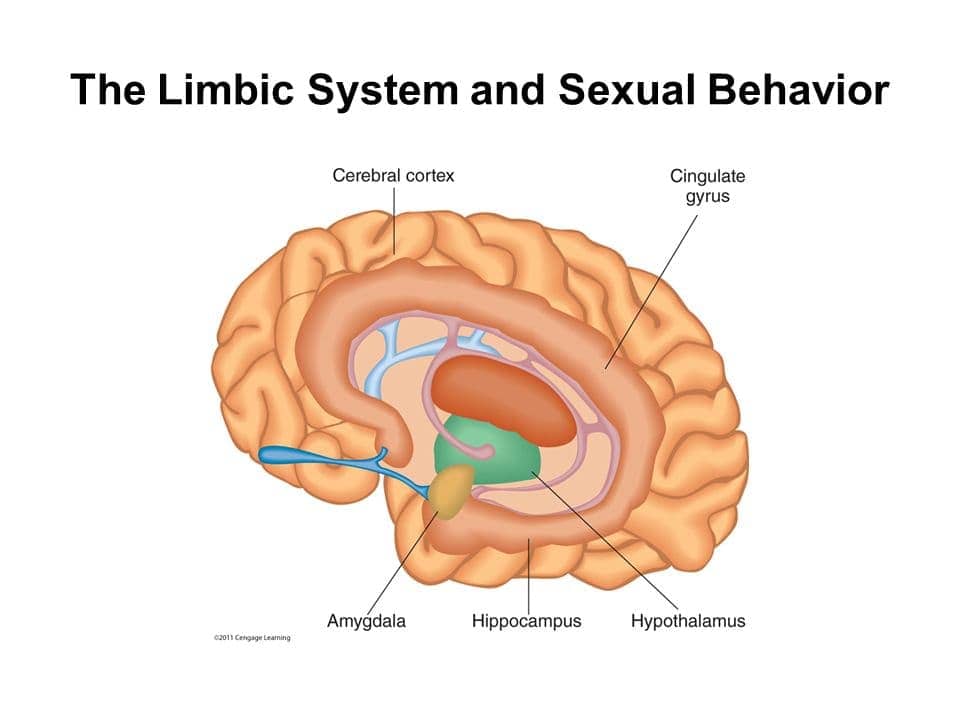
Hormones produced in endocrine system
- estrogen (women)
- testosterone (both)
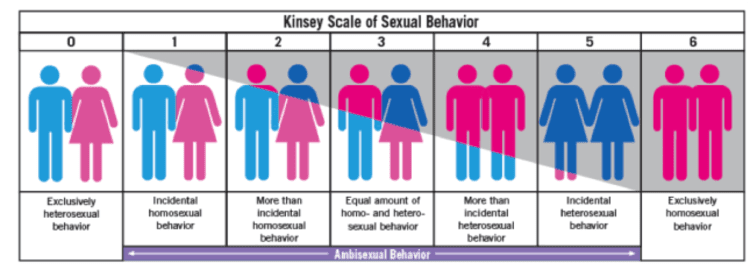
Dr. Alfred Kinsey
- Kinsey scale: used to categorize individual’s sexual orientation
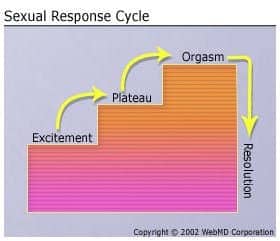
Masters and Johnson
- sexual response cycle: excitement, plateau, orgasm and resolution
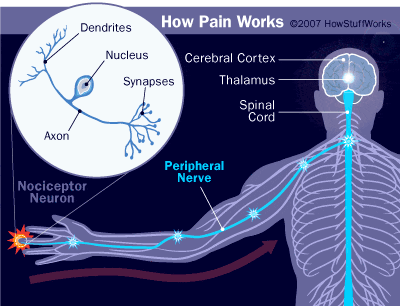
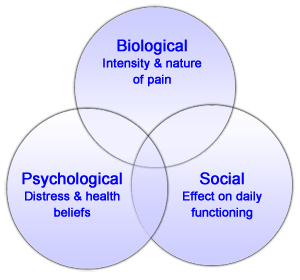
Biology of Pain
- Nociception process
- contact with stimulus
- reception: nerve ending sense stimulus
- transmission: relayed to central nervous system
- pain center reception: brain further processes
- Types of Pain
- Physical pain
- physical characteristics, intensity and interpretation
- acute vs chronic
- Social pain
- pain of social disconnection
- Psychological pain
- depression and other mental disorders
- Physical pain
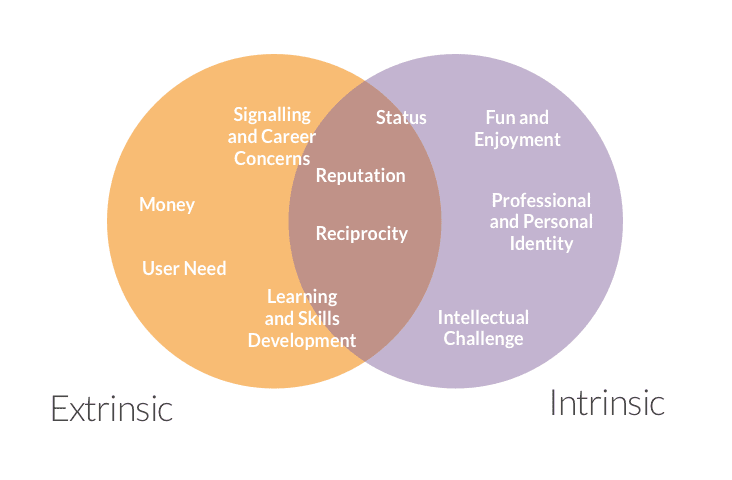
7.4 Social Motivation
- Human need to interact with others and be accepted by them
- extrinsic
- receive something from others
- intrinsic
- biological motives
- sense of personal satisfaction
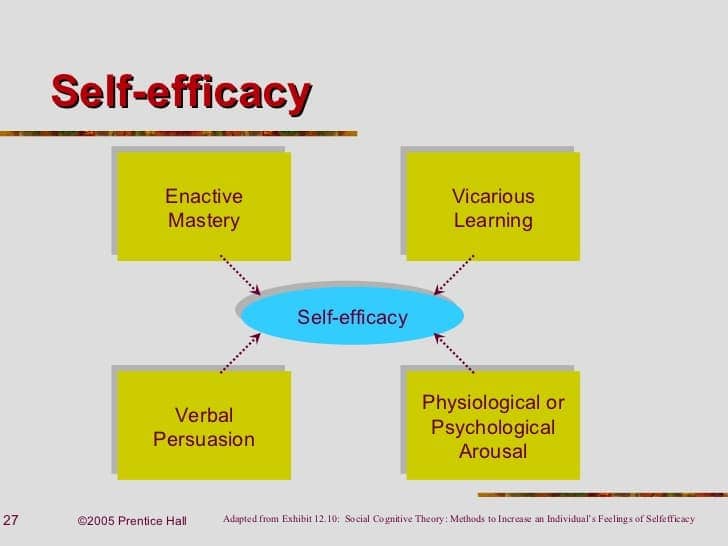
Albert Bandura
- We ultimately have a strong drive for self efficacy and that's what leads people to succeed
self-efficacy motivates behavior
Quiz
- Stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus will result in which of the following behaviors in laboratory rats?
- (A) An increase in sexual behavior
- (B) An increase in eating behavior
- (C) An increase in visual processing speed
- (D) A decrease in auditory perception
- (E) A decrease in memory functioning
- Which of the following is a disadvantage of relying on external rewards to motivate behavior?
- (A) There is potential to reduce extrinsic motivation
- (B) There is potential to reduce intrinsic motivation
- (C) It increases fear of failure
- (D) It increases fear of success
- (E) It decreases competency
- One theory of the effects of arousal holds that efficiency of behavior can be described as an inverted U-shaped function of increasing arousal. Which of the following accurately describes this relationship?
- (A) Greater arousal leads to better performance
- (B) Greater arousal leads to poorer performance
- (C) Low and high levels of arousal lead to poorest performance
- (D) Overarousal leads to performance efficiency
- (E) Underarousal leads to performance efficiency
- Which of the following presents a pair of needs from Abraham Maslow’s hierarchical need structure, in order from lower to higher need?
- (A) Belongingness, safety
- (B) Self-actualization, physiological needs
- (C) Physiological needs, safety
- (D) Esteem, belongingness
- (E) Self-actualization, esteem
- Which of the following scenarios best illustrates the facial feedback hypothesis of emotion?
- (A) Bill is a good card player who shows no emotion in his face that would reveal what he is thinking
- (B) Ellen says that hanging up the laundry on a clothesline makes her feel happy; she holds the clothespins in her teeth as she hangs each piece of clothing
- (C) Juanita fakes a smile to make her friends think she is happy
- (D) Paul has been blind from birth and has never seen emotional faces, but he has emotional facial expressions similar to those of a sighted person
- (E) As a result of Raj smiling at his customers, they smile at him
